Internet Information Services
IIS Supports HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, SMTP, NNTP
History
____________________________________________________________________________________________
O.SYSTEM IIS Ver Added Features
===================================================
Windows NT IIS 1.0
Windows NT IIS 2.0
Windows NT IIS 3.0 ->introduced the Active Server Pages dynamic scripting environment.[5]
Windows NT IIS 4.0
Windows 2000 IIS 5.0 -> introduced additional authentication methods, MMC-based administration application, support for the WebDAV , and enhancements to ASP.
Windows XP IIS 5.1
Windows 2003 IIS 6.0 included a new worker process model that increased security as well as reliability.
Windows2008 IIS 7.0 increased performance, simpler site deploys, Forms-based management application, new command-line management options
Windows2008 R2 IIS 7.5 IIS 7.5 improved WebDAV and FTP modules as well as command-line administration in PowerShell, introduced TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 support and process isolation for application pools.
Windows 8 IIS 8.0 Application Initialization, centralized SSL certificate support.
Windows2012 R2 IIS 8.5 Idle worker-Process page-out, Dynamic Site Activation, Enhanced Logging, ETW logging, and Automatic Certificate Rebind.
________________________________________________________________________________
Differences between Versions
_________________________________________________________________________________
IIS 6.0 Architecture:
IIS 7.0 Architecture:
________________________________________________________________________________
Differences between Versions
| IIS 4.0 | IIS 5.0 | IIS 5.1 | IIS 6.0 | |
Platform
|
Windows NT 4.0
|
Windows 2000
|
Windows XP Professional
|
Windows Server 2003 family
|
Architecture
|
32-bit
|
32-bit
|
32-bit and 64-bit
|
32-bit and 64-bit
|
Application process model
|
TCP/IP kernel
MTX.exe
|
TCP/IP kernel
DLLhost.exe (multiple DLL hosts in medium- or high-application isolation)
|
TCP/IP kernel
DLLhost.exe (multiple DLL hosts in medium- or high-application isolation)
|
HTTP.sys kernel
When IIS is running in IIS 5.0 isolation mode: Inetinfo.exe (for in-process applications) orDLLhost.exe (for out-of-process applications)
When IIS is running in Worker Process Isolation Mode: W3wp.exe (multiple worker processes)
|
Metabase configuration
|
Binary
|
Binary
|
Binary
|
XML
|
Security
|
Windows authentication
SSL
|
Windows authentication
SSL
Kerberos
|
Windows authentication
SSL
Kerberos
Security wizard
|
Windows authentication
SSL
Kerberos
Security wizard
Passport support
|
Remote administration
|
HTMLA
|
HTMLA
|
No HTMLA
Terminal Services
|
Remote Administration Tool (HTML)
Terminal Services
|
Cluster support
|
In Windows NT 4.0
|
IIS clustering
|
Windows support
|
Windows support
|
WWW services
|
IIS on Windows NT 4.0
|
Personal Web Manager on Windows 9x
IIS on Windows 2000
|
IIS optionally on Windows XP Professional
|
IIS on a member of the Windows Server 2003 family
|
_________________________________________________________________________________
IIS 6.0 Architecture:
1. Client requests for a page from the browser by hitting the site URL.
2. Request comes to kernel level. HTTP.SYS catches the requests and creates a separate queue for each and every application pool.
Note: Whenever we create an application pool, IIS automatically registers the pool with HTTP.SYS to identify it during request processing.
Then HTTP.SYS forwards the request to the Application Pool.
1. A request coming to the application pool means the worker process (w3wp.exe) starts action by loading the ISAPI Filter.
2. Based on the requested resource, w3wp.exe loads "aspnet_isapi.dll" for an APSX page and starts an HTTPRuntime which is the entry point of an application.
3. Then the HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest method signals the start of processing.
4. The HttpContext object represents the context of the currently active request, as it contains references to objects you can access during the request lifetime, such as Request, Response, Application, Server, and Cache.
5. The HttpRuntime creates a pool of HttpApplication objects.
6. The request passes through the HTTP Pipeline.
7. HTTP Modules are executed against the request until the request hits the ASP.NET page HTTP Handler.
8. Once the request leaves the HTTP Pipeline, the Page life cycle starts.
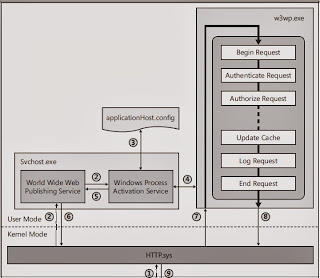
IIS 7.0 Architecture:
1.When a client browser initiates an HTTP request for a resource on the Web server, HTTP.sys intercepts the request.
2.HTTP.sys contacts WAS to obtain information from the configuration store.
3.WAS requests configuration information from the configuration store, applicationHost.config.
4.The WWW Service receives configuration information, such as application pool and site configuration.
5.The WWW Service uses the configuration information to configure HTTP.sys.
6.WAS starts a worker process for the application pool to which the request was made.
7.The worker process processes the request and returns a response to HTTP.sys.
The client receives a response.
IIS Services.
1) WWW Service : Which hosts websites
2) FTP Service : to upload and download and copy the files
3) SMTP Service : to Send and receive messages
4) NNTP Service : news
5) IIS Admin service: Metabase .
1.WWW Services:
The World Wide Web Publishing Service provides Web publishing for IIS, connecting client HTTP requests to Web sites running on an IIS-based Web server.The WWW service manages and configures the IIS core components that process HTTP requests. These core components include the HTTP protocol stack (HTTP.sys) and the worker processes .
2) FTP Service
IIS provides an FTP service, which you can use to allow users on remote computer systems to copy files to and from your server on a network that uses TCP/IP.
In IIS 6.0, the FTP service allows you to isolate users at the site level, a feature known as FTP user isolation, to help administrators secure and commercialize their Internet sites.
Because of the easy availability and wide adoption of FTP, Internet service providers (ISPs) and application service providers (ASPs) traditionally have used FTP to upload their Web content.
3) SMTP Service
The SMTP service in IIS processes messages by using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), which is a TCP/IP protocol that is used to send and receive messages from one computer to another on a network.
This protocol is used in intranets and on the Internet to route e-mail
4) NNTP Service
The Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) is an application protocol used for transporting Usenet news articles (netnews) between news servers and for reading and posting articles by end user client applications
5) IIS Admin service:
IIS Admin service is a Windows Server 2003 service that manages the IIS metabase.
The metabase stores IIS configuration data in a plaintext XML file that you can read and edit by using common text editors.
________________________________________________________________________________
IIS Authentications
- Anonymous authentication
- Basic access authentication
- Digest access authentication
- Integrated Windows Authentication
- UNC authentication
- .NET Passport Authentication (Removed in Windows Server 2008 and IIS 7.0)[12]
- Certificate authentication
- Anonymous authentication:
This authentication method allows everyone access to your Web sites, without asking for a user name or password. By default, this account is named IUSR_ComputerName and it is included in the Windows user group, Guests. This group has security restrictions.
2. Basic access authentication:
This authentication method prompts the user for a user name and a password, which are sent unencrypted over the network .
When you use Basic authentication, the browser displays a dialog box into which users are required to enter a previously assigned Windows account user name and password.The browser then attempts to establish a connection to a server using the user’s credentials.The plaintext password is Base64-encoded before it is sent over the network
3.Digest access authentication
This authentication method operates much like Basic authentication, except that passwords are sent as a hash value.
Digest authentication offers the same functionality as Basic authentication; however, Digest authentication provides a security improvement.Digest authentication sends credentials across the network as a Message Digest 5 (MD5) hash, which is also known as the MD5 message digest, in which the credentials cannot be decode from the hash .
4.Integrated Windows Authentication:
This authentication method uses hashing technology to identify your users Credentials.
Integrated Windows authentication (formerly called NTLM, and also known as Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication).Credentials are hashed before they are sent across the network.The client browser proves its knowledge of the password through a cryptographic exchange with your Web server, involving hashing ated Windows authentication uses Kerberos v5 authentication and NTLM authentication.
5.UNC authentication:
The UNC authentication method, which is also known as UNC Pass-through authentication, determines the credentials to use for gaining access to a UNC share on a remote computer.
Use IIS Manager to create a Web site or virtual directory and you specify a UNC path for the content, IIS Manager prompts to type a user name and a password for the network resource. The user name must be specified as domain\username. If you specify the details, both the UNCUserName Metabase Property and the UNCPassword Metabase Property are set. UNC authentication works by looking at the requesting the credentials that are stored in the UNCUserName and UNCPassword properties of the metabase to determine the credentials to pass through to the computer with the UNC share .
6 .NET Passport Authentication (Removed in Windows Server 2008 and IIS 7.0)
.NET Passport is a user-authentication service and a component of the .NET framework. The .NET Passport single sign-in service and express purchase service enable your business to deliver a fast, convenient, and secure way for consumers to sign in and make transactions on your site.
7.Certificate authentication:
Using SSl certificates.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Contents
1.Introduction
2.What is Webserver
3.Introduction to IIS
Overview of IIS
IIS version in Different OS's
How to Install IIS6.0
4.IIS 6.0 Process Model and Request Processing
5.Deploying your web sites on IIS
Creating a Virtual Directory.
Configuring a virtual directory
virtual Directory
Documents
ASP.NET
Directory Security
Custom Errors
6.Application Pool
How to Create application pool
Create New application pool
Create from an existing configuration file.
Configure Applicatin Pool properties
Recycling
what happens during application pool Recycling
Performance
Health
Identity.
7.Debugging your application that is Hosted on IIS.
1.Introduction
2.What is Webserver
3.Introduction to IIS
Overview of IIS
IIS version in Different OS's
How to Install IIS6.0
4.IIS 6.0 Process Model and Request Processing
5.Deploying your web sites on IIS
Creating a Virtual Directory.
Configuring a virtual directory
virtual Directory
Documents
ASP.NET
Directory Security
Custom Errors
6.Application Pool
How to Create application pool
Create New application pool
Create from an existing configuration file.
Configure Applicatin Pool properties
Recycling
what happens during application pool Recycling
Performance
Health
Identity.
7.Debugging your application that is Hosted on IIS.
_________________________________________________________________________________
IIS Installation 6.0
To install IIS, add components, or remove components using Control Panel
1. From the Start menu, click Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add or Remove Programs.
3. Click Add/Remove Windows Components.
4. In the Components list box, click Application Server.
5. Click Details.
6. Click Internet Information Services Manager.
7. Click Details to view the list of IIS optional components. select World wide web, SMTP AND NNTP
if required.
8. Select all optional components you wish to install.
IIS Installation 7.0
1.To install IIS, add components, or remove components using Control Panel
2. In the Control Panel, click Programs.
3. Click Turn Windows features on or off.
4.You may receive the Windows Security warning. Click Allow to continue. The Windows Features dialog box is displayed.
5. Expand Internet Information Services. Additional categories of IIS features are displayed. Select Internet Information Services to choose the default features for installation.
6. Expand the additional categories displayed, and select any additional features you want to install, such as Web Management Tools.
7.. If you are installing IIS for evaluation purposes, you may want to select additional features to install. Select the check boxes for all IIS features you want to install, and then click OK to start installation.
IIS Installation 7.5
1. Click Start -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> Server Manager.
2. In the Server Manager window, scroll down to Roles Summary, and then click Add Roles. The Add Roles Wizard will start with a Before You Begin page.
3. Select Web Server (IIS) on the Select Server Roles page. An introductory page will open with links for further information.
Note: When you use the Add Roles Wizard to install IIS, you get the default installation, which has a minimum set of role services. If you need additional IIS role services, such as Application Development or Health and Diagnostics, make sure to select the check boxes associated with those features in the Select Role Services page of the wizard.
4. Select the IIS services to be installed on the Select Role Services page. Add only the modules necessary. In this case, ASP.NET is selected, and a description of ASP.NET appears in the right pane. Once desired modules are added, click Next.
5. Add any required role services.
6. IIS is now installed with a default configuration for hosting ASP.NET on Windows Server. Click Close to complete the process.
7. Confirm that the Web server works by using http://localhost.
What is a Web Server
Visual
Studio has its own ASP.NET engine which is responsible for running your web
application so you don't have any problems running an ASP.NET application from
the VS IDE. When you want to host your site for others to access, the concept
of a "Web Server" comes into picture. A web server is responsible for
providing a response to requests that come from clients. So when multiple users
come in, multiple requests also come in and the web server will have a response
for each of them. IIS (Internet Information Server) is one of the most powerful
web servers from Microsoft that is used to host ASP.NET web applications. IIS
has its own ASP.NET Process to handle ASP.NET requests. If you look at this
picture:
The
first client will make a request to the web server (IIS), the web server checks
the request and will pass the request to the ASP.NET Process (don't get
confused here, I have explained the details), the ASP.NET process engine will
process the request and pass the response to the client via the web server. One
of the major roles of IIS is handling each and every request. Don't worry, I
have explained each and everything in more detail later. So far I hope it is
clear why we are using a web server.
Introduction to IIS
IIS
6.0 provides a redesigned World Wide Web Publishing Service architecture that
can help you achieve better performance, reliability, scalability, and security
for your web sites. In this section, I have described an overview of IIS and an
installation guide for IIS 6.0.
Overview of IIS
Internet Information Server
is one of the most powerful web servers provided by Microsoft that is able to
host and run your web applications. IIS supports the following protocols: FTP,
FTPS, SMTP, NNTP, HTTP/HTTPS. We can host our web sites on IIS, we can use it
as an FTP site also. For more information.
How to Install IIS 6.0
Installation
of IIS is very similar to installing any other system application from the
Control Panel. We have to start navigation from Control Panel > Add/Remove
Programs, then select Add/Remove Windows Component. Follow the screen given
below.
Select
"Application Server" from the checkbox list. This will open a new
window, select IIS, and click on OK.
This
will initiate IIS installation. The OS will show a continuous progress bar
during installation and will show a final message after installation is
complete.
Note: During the
installation period, it may ask for some OS files. You need to provide the paths
for them. After successful installation of IIS, go to Start > Run >
Inetmgr to launch IIS. The below screen will appear, which indicates that IIS
has been successfully installed in your system.
IIS 6.0 Process Model and Request Processing
Before
starting with a virtual directory and Application Pool and all other stuff, let
us have a quick look into the IIS 6.0 Process module and IIS request
processing. This topic is a huge one. Here I am just giving you an overview.
We
can divide the whole architecture into two layers.
1.Kernel Mode
2.Http.sys.
3.User Mode
4.Web Admin service
5.Virtual Directory
6.Application pool.
As
per the above diagram, IIS has two modes, Kernel and User. HTTP.SYS is the
heart of kernel mode which accepts raw requests from the client and pass it to
a particular application pool. Below are the steps of IIS request processing.
1. Client requests for a page from the browser by
hitting the site URL.
2. Request comes to kernel level. HTTP.SYS
catches the requests and creates a separate
queue for each and every application pool.
queue for each and every application pool.
Note: Whenever we create
an application pool, IIS automatically registers the pool with HTTP.SYS to
identify it during request processing.
Then
HTTP.SYS forwards the request to the Application Pool.
1. A request coming to the application pool means
the worker process (w3wp.exe) starts action by loading the ISAPI
Filter.
2. Based on the requested resource, w3wp.exe
loads "aspnet_isapi.dll" for an APSX page and starts an HTTPRuntime
which is the entry point of an application.
3. Then the HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest method signals the start of processing.
4. The HttpContext object represents the context of the
currently active request, as it contains references to objects you can access
during the request lifetime, such as Request, Response, Application, Server, and Cache.
5. The HttpRuntime creates a pool of HttpApplication
objects.
6. The request passes through the HTTP Pipeline.
7. HTTP Modules are executed against the request
until the request hits the ASP.NET page HTTP Handler.
8. Once the request leaves the HTTP Pipeline, the
Page life cycle starts.
IIS 7.0 Process Model and Request Processing
IIS 7.0 Process Model and Request Processing
The Diagram describes the request-processing flow that is shown in Figure 1:
1.When a client browser initiates an HTTP request for a resource on the Web server, HTTP.sys intercepts the request.
2.HTTP.sys contacts WAS to obtain information from the configuration store.
3.WAS requests configuration information from the configuration store, applicationHost.config.
4.The WWW Service receives configuration information, such as application pool and site configuration.
5.The WWW Service uses the configuration information to configure HTTP.sys.
6.WAS starts a worker process for the application pool to which the request was made.
7.The worker process processes the request and returns a response to HTTP.sys.
The client receives a response.
Deploying Web Sites on IIS
Creating a Virtual Directory
There
are various way to host a web application on IIS. Visual Studio has some
inbuilt features to host and create a virtual directory on IIS directly. Here is
one of my articles on hosting a site on IIS from Visual Studio. But in this
section, Idiscuss the basic steps for creating a virtual directory.
First,
right click on Default web sites > New > Virtual Directory.
By
selecting "Virtual Directory...", the virtual directory creation
wizard will start. Click on "Next".
Give
the "Alias" name and proceed for "Next". The alias name is
your virtual directory name.
As
its name implies, a "virtual directory" does not contain any physical
file. We need to define the physical file path that it will refer to. We have
to browse the physical path over here.
Now based on your requirements, you can select the check boxes and click
on "Next". Generally, we select only the "Read" option
Below
is a list of permissions that we can use:
·
Read: It is the most basic and is mandatory to
access webpages of your application.
·
Run
Scripts: It is required for
ASPX pages, not for static HTML pages because ASPX pages need more permissions
so they could conceivably perform operations.
·
Execute: This allows the user to run an ordinary
executable file or CGI application. This can be a security risk so only allow
when it is really needed.
·
Write: It allows to add, modify, or remove files
from the web server. This should never be allowed.
·
Browse: This allows one to retrieve a full list of
files in a virtual directory even if the contents of the files are restricted.
It is generally disabled.
You
are done! The virtual directory has been created successfully. You will get a
final message. Click on "Finish" to close the window and move
forward.
There
are other alternative options that you can use for creating a virtual
directory.
1. Copy the physical directory to the wwwroot
folder.
2. Physical Folder Properties > Web Sharing.
The
items listed below are very important for the configuration of any web
application.
·
Virtual Directory
·
Documents
·
Documents
·
ASP.NET
·
Directory Security
·
Custom Errors
I
have explained each of them step by step. Apart from them, a Virtual Directory
can have settings like BITS Server Extension, HTTP Header, etc. I haven't
covered those in this article. Let us start with the "Virtual
Directory" tab.
This
is the most important configuration section for a virtual directory. To open
this tab, we need to select the newly created virtual directory.
Right
click on it > Properties. The below screen will come up:
Here
we can change the local path (physical path). Before looking into other stuff,
first look into the "Application Settings" section. It seems the
application name is disabled. So first we need to click the "Create"
button, which will enable the rest of the settings. Check the below image.
Here
we can change the execution setting and application pool name. Choosing
"None" for Execute Permission will restrict the access to the web
site. Now we will move to the "Documents" tab.
The
Documents tab is used to set the default page of your web application. We can
add or remove the page name in this section. To configure, we have to move to
the "Documents" tab.
This
is useful when you want to access the site directly with the virtual directory
name. For example, if your virtual directory name is "mywebsite" and
your home page name is "home.aspx", then you can access the
page as follows:
http://<ip>/mywebsite/home.aspx
but
if you define home.aspx in the Documents section, you need to only use
this at the address bar to access the site:
http://<ip>/mywebsite
ASP.NET
If
IIS is registered with multiple .NET Framework versions, the ASP.NET version
dropdown list shows all of them. But based on the application, we need to
change the framework version. E.g.: If our application was developed in .NET
2.0, then the version should be 2.0.X.X.
Tip: If .NET Framework is
already installed in your system when you are installing IIS, then ASP.NET will
not be registered with IIS. So if you host an application on IIS, it will not
work. To register IIS with the ASP.NET version, you need to run the aspnet_regiis
-i command from the command prompt. This will automatically register the
.NET Framework with your IIS.
Directory Security
Directory
security enables all kinds of security access for your web application. For
directory, we need to move to the "Directory Security" tab.
Click
on the "Edit" button to modify the directory security settings. After
clicking on the Edit button, the below screen will come up.
Below
are the commonly used IIS security settings:
·
Anonymous
·
Integrated Windows
Authentication
·
Basic Authentication
·
Digest Authentication
Anonymous
Anonymous
authentication means the site is accessible to all. This is the default
authentication mode for any site that is hosted on IIS, and it runs under the
"IUSR_[ServerName]" account. We can change it by clicking on the
"Browse" button.
Integrated Windows Authentication
This
authentication mode is generally used for Intranet sites. Users are
authenticated from the Active Directory. Integrated Windows authentication is
also known as NTLM authentication. If browser settings automatically login for
trusted sites for Windows authentication then the site will be logged in
automatically with the Windows user credentials.
Basic Authentication
This
is supported by all browsers and is a part of the HTTP standard. This shows a
login dialog control which accepts the user name and password. The user ID and
password are passed to IIS to authenticate the user from the Windows
credentials.
Digest Authentication
The
disadvantages of Basic authentication mode is that it sends a password as plain
text. Digest authentication does almost the same thing as basic authentication
but it sends the "hash" of the password rather than sending plain
text.
Integrated
Windows, Basic Authentication, and Digest Authentication use Active Directory
to authenticate the user.
Note: There are many
things related with IIS and ASP.NET Security configuration. I am not covering
all these in detail. I am just giving a brief overview so that you are
comfortable with all this stuff.
For
configuring SSL, please read the reference link that I have provided in the
References section.
The
Custom Errors tab allows us to specify the error page that will be displayed
for any specific type of HTTP Error.
We
can also customize the setting at our application level by configuring the web.config
settings or changing the htm file path by clicking on the
"Edit" button.
Application Pool
Application
pool is the heart of a website. An Application Pool can contain multiple web
sites. Application pools are used to separate sets of IIS worker processes that
share the same configuration. Application pools enable us to isolate our web
application for better security, reliability, and availability. The worker
process serves as the process boundary that separates each application pool so
that when a worker process or application is having an issue or recycles, other
applications or worker processes are not affected.
Generally
we do it in our production environment. The main advantages of using an
application pool is the isolation of worker processes to differentiate sites
and we can customize the configuration for each application to achieve a
certain level of performance. The maximum number of application pools that is
supported by IIS is 2000.
In
this section, I have discussed about the creation of application pools,
application pool settings, and assigning an application pool to a web site.
Application
pool creation in IIS 6.0 is a very simple task. There are two different ways by
which we can create an application pool. There is a pre-defined application
pool available in IIS 6.0, called "DefaultApplicationPool". Below are
the two ways to create an application pool:
·
Create New Application
Pool
·
Create From Existing
Configuration File
First
of all, we need to open the IIS Configuration Manager. Then right click on
Application Pool and go to New > Application Pool.
The
below screen will appear, where we need to mention the application pool name.
When
we create a new application pool, we can use the default application setting
for it. The selection of "Default Settings" means by default the
application pool setting will be the same as the IIS default settings. If we
want to use the configuration of an existing application pool, we need to
select the section option "Use existing application pool as
template". Selecting this option will enable the application pool name
dropdown.
If
we select an existing application pool as a template, the newly created
application pool should have the same configuration of the template application
pool. This reduces the time for application pool configuration.
That
is all about creating a new application pool. Now let us have a look at the
creation of an application pool from an existing XML configuration file.
Create From Existing Configuration File
We
can save the configuration of an application pool into an XML file and create a
new application pool from that. This is very useful during the configuration of
an application pool in a Web Farm where you have multiple web servers and you
need to configure the application pool for each and every server. When you are
running your web application on a Load Balancer, you need to uniquely configure
your application pool.
So
first of all, you need to save the application pool configuration in a server.
Check the below image for details.
During
this operation, we can set the password for the configuration file which will
be asked during the import of the application pool on another server. When we
click on "Save Configuration to a file", the below screen will
appear.
Where
we need to provide the file name and location. If we want, we can set a
password to encrypt the XML file. Below is a part of that XML:
Location ="inherited:/LM/W3SVC/AppPools/StateServerAppPool"
AdminACL="49634462f0000000a4000000400b1237aecdc1b1c110e38d00"
AllowKeepAlive="TRUE"
AnonymousUserName="IUSR_LocalSystem"
AnonymousUserPass="496344627000000024d680000000076c20200000000"
AppAllowClientDebug="FALSE"
AppAllowDebugging="FALSE"
AppPoolId="DefaultAppPool"
AppPoolIdentityType="2"
AppPoolQueueLength="1000"
AspAllowOutOfProcComponents="TRUE"
AspAllowSessionState="TRUE"
AspAppServiceFlags="0"
AspBufferingLimit="4194304"
AspBufferingOn="TRUE"
AspCalcLineNumber="TRUE"
AspCodepage="0"pre>
Now
we can create a new application pool for this configuration file. While
creating a new application pool, we have to select the "Application Pool (
From File )" option as shown in the below figure.
When
we select this option, a screen will come where we need to enter the file name
and the password of that file.
Select
the file and click on the "Read File" button. This will show you the
imported application pool name. Click "OK" to import the full
configuration.
Here
we need to mention the new application pool name or we can have another option
where we can replace an existing application pool. For moving ahead, we need to
provide the password.
This
is the last step for creating a new application pool from an existing
configuration file.
This
is one of the most important tasks for web server configuration and this is important
when we are hosting on a production server. As I have already discussed, the
application pool is the heart of any web application hosted on IIS. We need to
know each and every configuration of the application pool. To start
configuration, we need to go to the Properties of the application pool.
We
need to configure the following things in the application pool:
·
Recycling
·
Performance
·
Health
·
Identity
Recycling
the application pool means recycling the worker process (w3wp.exe) and
the memory used for the web application. It is a very good practice to recycle
the worker process periodically, which wll keep the application running smooth.
There are two types of recycling related with the application pool:
·
Recycling Worker
Process - Predefined settings
·
Recycling Worker
Process - Based on memory
Recycling Worker Process - Predefined Settings
Worker
process recycling is the replacing of the instance of the application in
memory. IIS 6.0 can automatically recycle worker processes by restarting the
worker processes that are assigned to an application pool and associated with
websites. This improves web site performance and keeps web sites up and running
smoothly.
There
are three types of settings available for recycling worker processes:
·
In minutes
·
Number of requests
·
At a given time
Recycle Worker Process (In Minutes)
We
can set a specific time period after which a worker process will be recycled.
IIS will take care of all the current running requests.
Recycle Worker Process (Number of Requests)
We
can configure an application with a given number of requests. Once IIS reaches
that limit, the worker process will be recycled automatically.
Recycle Worker Process (In Minutes)
If
we want to recycle the worker process at any given time, we can do that
configuration on IIS. We can also set multiple times for this.
Recycling Worker Process - Based on Memory
Server
memory is a big concern for any web application. Sometimes we need to clean up
a worker process based on the memory consumed by it. There are two types of
settings that we can configure in the application pool to recycle a worker
process based on memory consumption. These are:
·
Maximum virtual memory
used
·
Maximum used memory
At
any time, if the worker process consumes the specified memory (at memory
recycling settings), it will be recycled automatically.
This
is quite an interesting question. Based on the above settings, an application
pool can be recycled any time. So what happens to the users who are accessing
the site at that time? We do not need to worry about that. This process is
transparent from the client. When you recycle an application pool, HTTP.SYS
holds onto the client connection in kernel mode while the user mode worker
process recycles. After the process recycles, HTTP.SYS transparently routes the
new requests to the new worker process.
Moving
to the Performance tab in the Properties dialog box results in the following
output.
To
improve the performance of a web application, we can setup the performance
settings of the application pool. We can set the shut down time of the worker
process based on the ideal time. The worker process will be shut down at a
given time period if it is ideal. Whenever a new requests comes, it will live
again. Another important thing for improving the performance is "Web
Garden".
Web Garden
Overview of Web Garden
By
default, each application pool runs with a single worker process (W3Wp.exe). We
can assign multiple worker processes with a single application pool. An
application pool with multiple worker processes is called a Web Garden. Many
worker processes with the same application pool can sometimes provide better
throughput performance and application response time. And each worker process
should have its own thread and memory space.
As
Shown in the picture, in IIS Server, there may be multiple application pools
and each application pool has at least a single worker process. A Web Garden
should contain multiple worker processes.
There
are certain restrictions in using a Web Garden with your web application. If we
use Session Mode as "in proc", our application will not work
correctly because the Session will be handled by a different worker process. To
avoid this, we should use Session Mode as "out proc" and we can use
"Session State Server" or "SQL-Server Session State".
How to Create a Web Garden?
We
need to increase the number of worker processes on the Performance tab.
Main advantage: The worker processes in a web garden share the requests that
arrive for that particular application pool. If a worker process fails, another
worker process can continue processing the requests.
Now
we move to the "Health" tab. When wel select the "Health"
tab, it will show the following screen:
IIS
provides a couple of settings to improve the health of an application pool.
There are also a few settings for measuring the worker process health. These
are:
·
Enable Pinging
·
Enable Rapid-fail
protection
·
Startup time limit
·
Shutdown time limit
Enable Pinging
This
property specifies whether the WWW Publishing Service should periodically
monitor the health of a worker process. Checking this option indicates to the
WWW service to monitor the worker processes to ensure that worker processes are
running and healthy. By default, it sets to 30s. This is also needed to check
if a service is staying ideal or not. If it is ideal it can be shutdown until
the next request comes. The Windows Activation Process maintains all this
stuff.
Enable Rapid-fail Protection
When
enabling Rapid Fail Protection, the application pool is shut down if there are
a specified number of worker process crashing within a specified time period.
When this happens, the WWW Publishing Service puts all applications in the
application pool "out of service".
Failure Count: The default value for failure count is 5 minutes. This
property specifies the maximum number of failures allowed within the number of
minutes specified by the "Time Period" property before the
application pool is shut down by Rapid Fail Protection. If the number of
failure is more than the specified in a given time, the application pool should
be put on "out of service mode".
Time period:
This property specifies the number of minutes before the failure count for a
process is reset. By default, it is set to 5 minutes.
Startup time limit
The
Start up time limit property specifies the amount of time that the WWW
Publishing Service should wait for a worker process to finish starting up and
reporting to the WWW Service. In general it means the time taken to start a
worker process.
Shutdown time limit
This
is the shutdown time for a worker process. This is the time required to execute
all old running worker process requests before it shuts down during recycle
time.
This
is the last and final setting for an application pool. An application pool has
three types of identity: "Network Service" is the default Identify.
"defaultappPool" also runs under the "Network Service"
Identity. Below are the listed application pool identities with description:
Identity Description
LocalSystem : A built-in account that has administrative privileges on the server. It can access both local and remote resources. For any kind accessing of server files or resources, we have to set the Identity of the application pool to Local System.
LocalServices : Built-in account has privileges of an authenticated local user account. It does not have any network access permission.
NetworkService : This is the default Identity of an application pool. NetworkServices has privileges of an authenticated local user account.
Navigating
to the Identity tab will show the following screen:
We
can also configure the application pool under a given user account. For that,
we need to select the "Configurable" option on "Identity"
tab.
This
is all about the application pool. Hope now you have a very good understanding
on what application pool is, how to create and configure the application pool.
Q: You are using a file
upload control in your web application and it is working fine on Visual Studio
but when you host the same code on IIS, it is not working. This is a very
common problem in web hosting when file upload is involved.
A: When a web
application runs under Visual Studio - ASP.NET engine integrated with visual
studio takes care of all the executions. And this engine has sufficient rights
so that it can write data on your disk. But when you host the site on IIS, as I
have already mentioned, it runs under the "Network Services"
Identity, which has very minimum rights on your system. The user can only have
read access on the site. So for resolving file upload issues, you need to
change the Identity of the application pool from "Network Service" to
"Local System". Local System identity means the client can have write
access on your hard drive. This will resolve your issue of file uploading on
the server.
You
can also resolve this issue by giving Write access permission to the file
destination folder for "Everyone".
Enabling Web Service Extension
IIS
6.0 provides a certain type of configuration from where we can enable/disable
web service extensions. If we want to prohibit/restrict any kind of extension,
we need to select the extension and click on the "Prohibit" button.
Note: If the ASP.NET v
2.0.X.XXXX extension is prohibited over here, you will not be able to access NET
2.0.the site which is running on .
If
your site is hosted on IIS and we want to debug the site, the main thing that
we need to do is attach a worker process with Visual Studio. There are two
possible scenarios for debugging from IIS:
1. Site is hosted on local IIS server: Local
IIS debugging
2. Site is hosted on remote IIS server:
Remote IIS debugging










































No comments:
Post a Comment